How Does NeuroStar TMS Treatment Work at Reliant Family Psychiatry in Grand Prairie, TX.
Reliant Family Psychiatry offers NeuroStar Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS), a non-invasive, FDA-approved therapy for depression, OCD, and smoking cessation, showing potential in treating anxiety and PTSD.
Effective especially for treatment-resistant depression, TMS uses magnetic fields to stimulate brain cells. Treatment involves pain-free daily sessions over 4-6 weeks, with no lasting side effects.
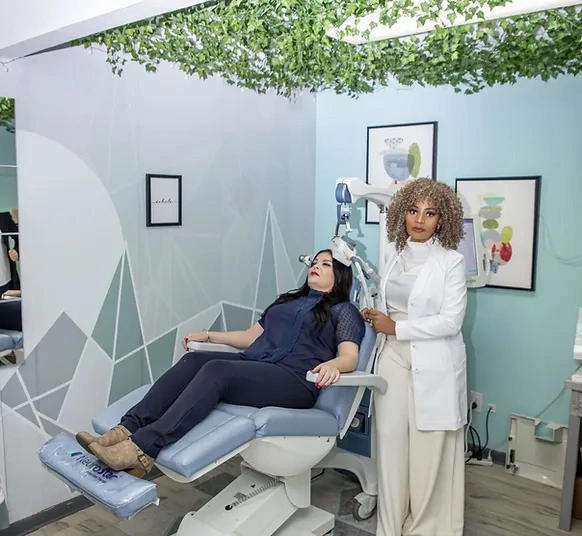
NeuroStar TMS Treatment For Depression, Anxiety Disorders & PTSD.
Healthcare professionals tailor the application of TMS based on the specific ailment they are addressing. For individuals grappling with clinical depression, the usual target is the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex on the brain’s left side, as approved by the FDA.
Encouraged by TMS’s effectiveness in treating depression, researchers have widened their scope to include its application for anxiety, PTSD, and a variety of other neurological and psychiatric disorders.
For those battling anxiety, particularly those who have found limited relief from cognitive therapies or medication, TMS emerges as a potentially transformative option. At Reliant Family Psychiatry, we extend TMS treatments for anxiety, OCD, PTSD, and clinical depression.
NeuroStar TMS and Major Depression
Many people with Major depression have less active brains in an area called the prefrontal cortex. This part of the brain helps control how we feel and deal with pain. Transcranial magnetic stimulation therapy, or TMS, helps wake up the nerve cells in this area, making the brain more active.
When someone asks, “Does TMS really work?” it’s good to know that a lot of research shows it can help treat depression, especially if other treatments haven’t helped. About half of the people who haven’t gotten better with other depression treatments feel better or even completely recover after trying TMS.

NeuroStar TMS and Anxiety Disorders
When someone is feeling depressed, their prefrontal cortex (a part of the brain that helps with feelings and pain) isn’t as active as it should be. But with anxiety, it’s a different story. People with anxiety have a part of their brain called the amygdala that’s too active. So, in this case, the magnetic energy does not have to activate but slow down a particular brain region.
TMS works with low and high frequencies. To slow down brain activity, low-frequency magnetic pulses are used. Repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation treats anxiety by lowering nerve cells to normal activity levels.
NeuroStar TMS and Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD)
People with OCD often have parts of their brain working overtime, which causes them to repeat the same actions or thoughts again and again. rTMS therapy aims to calm these overly busy brain areas, helping to keep things in balance.
Besides treating OCD and anxiety, TMS therapy is also helpful for conditions like autism, PTSD, chronic pain, and more. These days, scientists are really seeing how useful NeuroStar therapy can be, especially for conditions that don’t respond well to regular medicines or talking therapies.
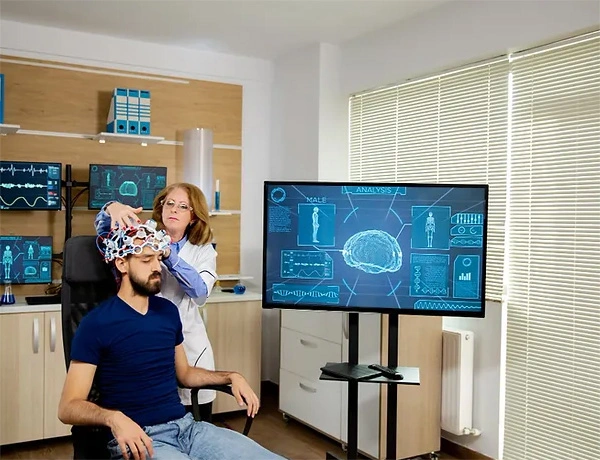
What To Expect During TMS Treatments
Before we start a treatment plan to help heal your emotional, mental, or physical struggles, we need to understand what’s going on in your mind and body. Some people come to us already knowing their diagnosis, while others aren’t sure why they feel the way they do. So, the first thing we do is an evaluation.
Many people worry when they hear the words ‘psychiatric’ or ‘psychological’ evaluation. Unfortunately, there are a lot of stigmas and misconceptions surrounding these terms. When we say that the first part of your treatment consists of completing a psychiatric evaluation or a psychological assessment, our goal is to understand your needs a little bit better.
What happens in this first step? We’ll ask about your current symptoms, how long you’ve had them, any past treatments you’ve tried, and your hopes for the future – like your dreams and goals. We might also ask about any diagnoses you’ve had and your family’s health history.
We understand that talking about your life may feel uncomfortable, but rest assured that we will not push you to share information you are not ready to share. Our goal is to promote your mental wellness and help you manage your symptoms.
Once we have a clearer picture of your mental, emotional, and physical state, we’ll create a TMS treatment plan tailored for you, aiming to give you lasting relief and improvement.
Benefits of TMS Therapy
Numerous benefits are associated with TMS therapy. For example, TMS therapy is beneficial because:
- 1. It is a non-invasive and well-tolerated treatment.
- 2. It does not require anesthesia.
- 3. It does not require hospitalization.
- 4. Studies support that TMS treatments cause few to no side effects.
- 5. You can go to the TMS sessions and drive back home by yourself.
- 6. You will be able to continue with your daily routines during the length of your treatment, including work and college.
- 7. TMS therapy also works well with other types of talk therapies and treatments.
Side Effects Of NeuroStar TMS Treatment
Potential Side Effects of TMS Therapy
-
Generally causes few or no side effects.
Minor side effects might occur but typically go away quickly after treatment. - Treatment effectiveness is not affected by these side effects.
- Side Effects Of NeuroStar TMS Treatment
Issues for People with Hypersensitivity
- Some report hearing problems due to TMS machine noise.
- Earplugs are provided to prevent hearing issues.
- Any concerns should be discussed with your doctor.
- Symptoms, if they occur, resolve soon after a TMS session.
- No long-term side effects have been reported from rTMS therapy.
Important Considerations for Specific Cases
- Pregnant individuals or those with a history of brain injury, brain damage, seizures, or epilepsy should consult their TMS physician before starting treatment.
- Presence of metal implants (like electrodes, aneurysm clips, bullet fragments, deep brain stimulators) in the brain-head-neck area should be reported.
- Discuss past and current medical and mental health history, including medications, with your TMS physician to ensure the suitability of the treatment.
NeuroStar TMS Painless Treatment , FDA-Approved Therapy
FDA-Endorsed, Non-Invasive Treatment TMS stands out as a non-intrusive, FDA-sanctioned therapy, offering a more comfortable experience with fewer side effects compared to traditional antidepressants. During the session, you remain fully awake and can freely talk with your therapist. The FDA for the treatment of major depressive disorder, OCD, smoking cessation and anxiety symptoms in people with depression.
The magnetic waves used in TMS therapy penetrate just about two to three centimeters beneath the brain’s surface, directly under the treatment coil. The pulses are focused to maximize effects on other brain areas connected to the area of stimulation, to have a larger therapeutic effect.

Drug-free Depression Treatment that Works For You
What to say:
Research involving over 14,000 individuals who underwent NeuroStar treatments revealed significant improvements in alleviating depression symptoms. Furthermore, a majority of these patients achieved complete relief from their symptoms following the completion of the prescribed treatment regimen.
What to know:
– 83% of patients completing NeuroStar treatment experienced measurable
depression relief*9
– 62% experienced full remission of their depression symptoms
– Patients may have been prescribed concomitant depression treatments including
medication
Effectiveness of TMS in Treating Depression:
(TMS) has emerged as a highly effective treatment for depression, particularly in cases where traditional therapies have failed. Clinical studies, including those conducted by institutions like Stanford University, have demonstrated remarkable success rates.
For instance, an intensive form of TMS known as SAINT achieved remission in 79% of participants with severe depression, often within days of treatment. Moreover, about 78.6% of individuals with treatment-resistant depression responded positively to TMS, showcasing its potential as a lifesaver for those hardest hit by this condition.
Traditional TMS treatments also report significant improvement, with around half of the patients showing improvement and a third experiencing remission. These findings position TMS as a transformative option in the fight against depression, offering hope and relief to many who have struggled with conventional treatments.
read more https://med.stanford.edu/news/all-news/2021/10/depression-treatment.html
Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS) at Reliant Family Psychiatry offers a promising alternative for individuals struggling with depression, particularly for those who have not responded to other treatments. With its non-invasive nature and proven effectiveness, TMS is changing the landscape of depression treatment, offering hope and improved quality of life to many.

Discover a brighter mental well-being journey at Reliant Family Psychiatry in Texas!
- We're here to guide you every step of the way. Choose Reliant Family Psychiatry today

